9. PCIe¶
9.1. Introduction¶
There is 1 PCIe3.0 x 4 interface on the AIO-3588Q development board, as shown in the figure:
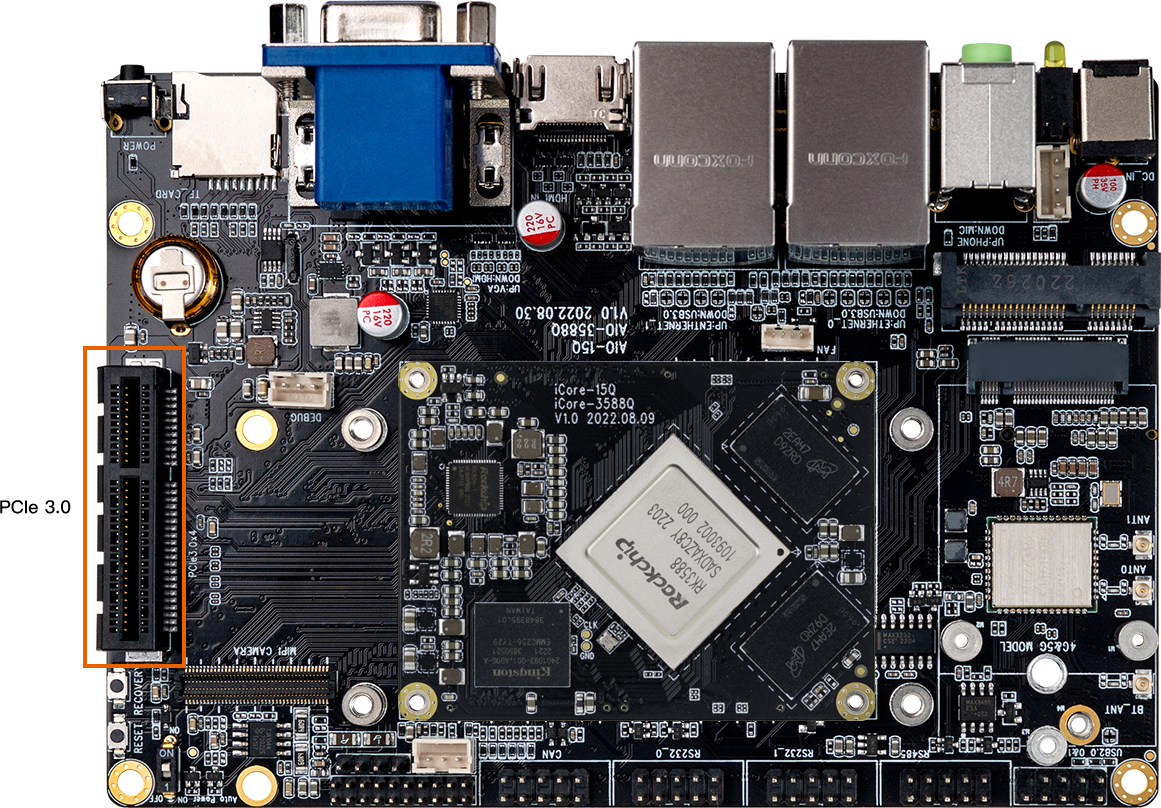
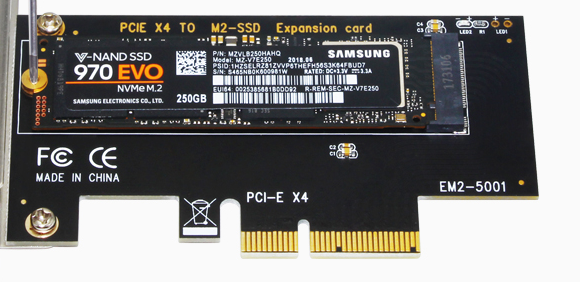
It can be inserted into the NVME protocol M.2 to PCIe3.0 x 4 adapter board + NVME protocol M.2 SSD for use, as shown in the figure:
9.2. Software configuration¶
The available hardware resources of RK3588 PCIe and the corresponding relationship between the pcie controller node and PHY node on the software are shown in the figure:
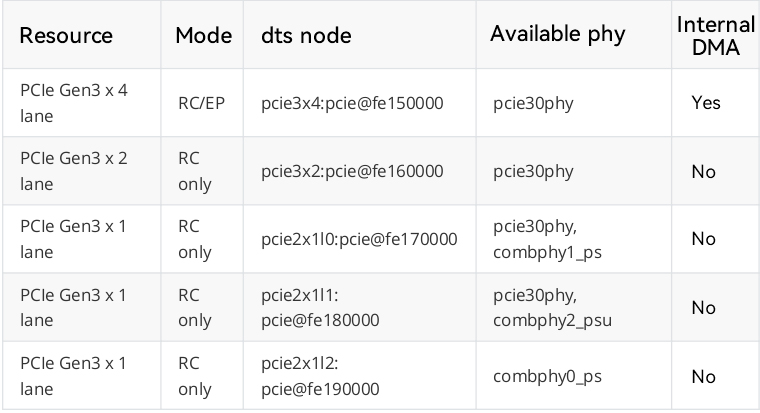
The PCIe3.0 x 4 interface on the AIO-3588Q development board uses the PCIe Gen3 x 4 lane set of resources of the RK3588.
9.2.1. DTS configuration¶
Generally, configure the power supply pin and reset pin in DTS according to the schematic diagram, and select the correct pcie controller node and PHY node to enable.
There is the following configuration in kernel-5.10/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dtsi:
/* pcie3.0 x 4 slot */
&pcie30phy {
status = "okay";
};
&pcie3x4 {
reset-gpios = <&gpio4 RK_PB6 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>;
vpcie3v3-supply = <&vcc3v3_pcie30>;
status = "okay";
};
&vcc3v3_pcie30{
gpios = <&gpio4 RK_PC6 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>;
startup-delay-us = <5000>;
status = "okay";
};
pcie30phy:PHY node
pcie3x4:pcie3x4 controller node
reset-gpios:reset pin properties
vcc3v3_pcie30:power supply pin node
9.3. Mount¶
9.3.1. Auto mount¶
Format the hard drive to a usable format in the Android system interface to mount it automatically at boot
9.3.2. Command to mount manually¶
Find device nodes
ls /dev/block/nvme*
/dev/block/nvme0n1
Formatted as EXT4 file format
mkfs.ext4 /dev/block/nvme0n1
Mount
mount /dev/block/nvme0n1 /mnt/media_rw/
View the mount path
df -h
/dev/block/nvme0n1 916G 24K 916G 1% /mnt/media_rw
or
cat /proc/mounts | grep nvme
/dev/block/nvme0n1 /mnt/media_rw ext4 rw,seclabel,relatime 0 0
9.4. Read and write speed¶
The transfer rate of PCIe3.0 x 4 is theoretically 4 GB/s. You can refer to the following commands to test the read and write speed:
dd
# The path is modified according to the actual mount path
# Write 1G file
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
busybox dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/media_rw/41AD-09EA/test1 bs=1M count=1024 conv=sync
# Read 1G file
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
busybox dd if=/mnt/media_rw/41AD-09EA/test1 of=/dev/null conv=sync
fio
# Using fio will format the hard drive
# Write
fio -filename=/dev/block/nvme0n1 -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=write -ioengine=psync -bs=1M -size=200G -numjobs=30 -runtime=60 -group_reporting -name=mytes
# Read
fio -filename=/dev/block/nvme0n1 -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=read -ioengine=psync -bs=1M -size=200G -numjobs=30 -runtime=60 -group_reporting -name=mytes
