1. Camera¶
Hardware interface
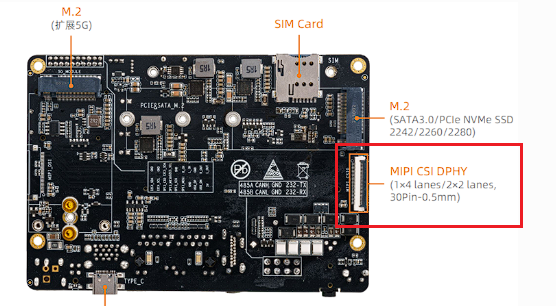
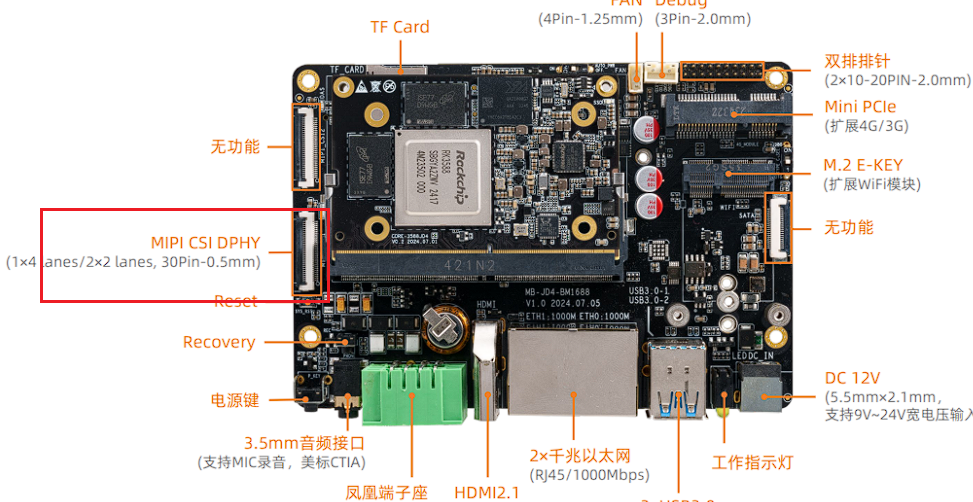
AIO-3588JD4 The default firmware only enables the MIPI_CSI0 camera. CSI0/1 share the same i2c group and need to configure gpio port to switching. If two MIPI_CSI are used at the same time, the sensor driver needs to be modified to support dynamic switching.
1.1. MIPI CSI¶
RK3588/RK3588S platform has two physical mipi dphy, include dphy0_hw/dphy1_hw .It can work in two modes: full mode and split mode; and split into three logical dphy: csi2_dphy0, csi2_dphy1, csi2_dphy2 (See detail in rk3588.dtsi)
1.1.1. Full Mode¶
Only use csi2_dphy0 (csi2_dphy0 and csi2_dphy1/csi2_dphy2 cannot be used at the same time);
Maximum 4 data lanes;
Maximum speed 2.5Gbps/lane;
1.1.2. Split Mode¶
Use csi2_dphy1 and/or csi2_dphy2, cannot use csi2_dphy0 at this mode;
csi2_dphy1 and csi2_dphy2 can be used at the same time;
csi2_dphy1 and csi2_dphy2 both have maximum 2 data lanes;
csi2_dphy1 maps to physical dphy lane0/lane1;
csi2_dphy2 maps to physical dphy lane2/lane3;
Maximum speed 2.5Gbps/lane
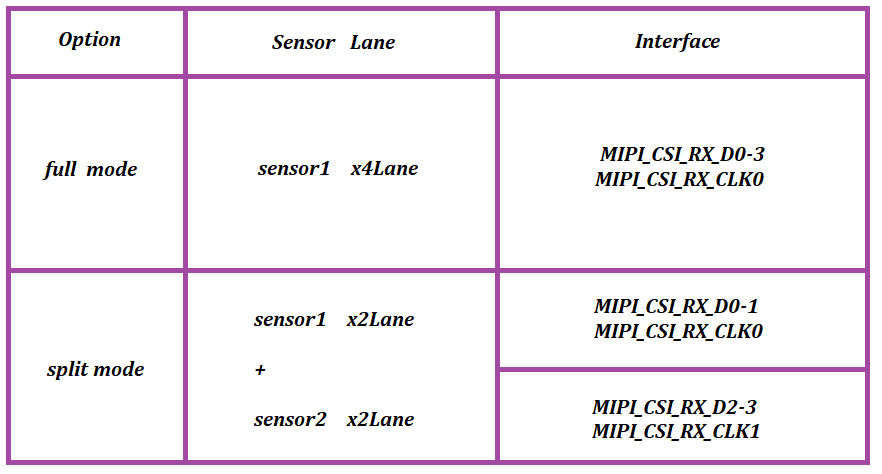
In short, if we use single-camera, we can set dphy to full mode, if we use dual-camera, we can set dphy to split mode.
1.2. Full Mode Configuration¶
Link path: sensor->csi2_dphy0->mipi2_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds2 - - -> rkcif_mipi_lvds2_sditf->rkisp0_vir0
1.2.1. Full Mode DTS Configuration Key Points¶
1.2.2. Configure Sensor¶
We need to check the MIPI CSI interface in schematic to find out which I2C bus is used for camera sensor. And configure the camera under that I2C node, correctly set the properties like I2C device address, pins, etc. For example, there’s a configuration for xc7160 in Core-3588JD4:
1.2.3. Configure Logical Dphy¶
csi2_dphy0 and csi2_dphy1/csi2_dphy2 cannot be used at the same time. In addition, we need to enable csi2_dphy0_hw node.
&csi2_dphy0 {
status = "okay";
ports {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
port@0 {
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipidphy0_in_ucam0: endpoint@1 {
reg = <1>;
remote-endpoint = <&xc7160_out0>;
data-lanes = <1 2 3 4>;
};
};
port@1 {
reg = <1>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
csidphy0_out: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&mipi2_csi2_input>;
};
};
};
};
&csi2_dphy0_hw {
status = "okay";
};
&mipi2_csi2 {
status = "okay";
ports {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
port@0 {
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi2_csi2_input: endpoint@1 {
reg = <1>;
remote-endpoint = <&csidphy0_out>;
};
};
port@1 {
reg = <1>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi2_csi2_output: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&cif_mipi2_in0>;
};
};
};
};
&rkcif {
status = "okay";
};
&rkcif_mmu {
status = "okay";
};
&rkcif_mipi_lvds2 {
status = "okay";
port {
cif_mipi2_in0: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&mipi2_csi2_output>;
};
};
};
1.2.4. Configure Isp¶
The remote-endpoint in rkisp_vir0 node should point to mipi_lvds2_sditf
sensor xc7160 have its own ISP, so rkisp is not required.In other cases, the sensor defaults to the following configuration
&rkcif_mipi_lvds2_sditf {
status = "disabled";
port {
mipi_lvds2_sditf: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&isp0_vir0>;
};
};
};
&rkisp0 {
status = "disabled";
};
&isp0_mmu {
status = "disabled";
};
&rkisp0_vir0 {
status = "disabled";
port {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
isp0_vir0: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&mipi_lvds2_sditf>;
};
};
};
1.3. Split Mode Configuration¶
Link path:
sensor1->csi2_dphy1->mipi2_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds2 - - -> rkcif_mipi_lvds2_sditf->rkisp0_vir2
sensor2->csi2_dphy2->mipi3_csi2->rkcif_mipi_lvds3 - - -> rkcif_mipi_lvds3_sditf->rkisp1_vir0
1.3.1. Split Mode DTS Configuration Key Points¶
1.3.2. Configure Sensor¶
We need to check the MIPI CSI interface in schematic to find out which I2C bus is used for camera sensor. And configure the camera under that I2C node, correctly set the properties like I2C device address, pins, etc. For example, there’s a configuration for gc2053/gc2093 in Core-3588JD4:
1.3.3. Configure csi2_dphy1/csi2_dphy2¶
csi2_dphy0 and csi2_dphy1/csi2_dphy2 cannot be used at the same time.
&csi2_dphy0_hw {
status = "okay";
};
&csi2_dphy1 {
status = "okay";
ports {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
port@0 {
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi_in_ucam2: endpoint@1 {
reg = <1>;
remote-endpoint = <&gc2053_out2>;
data-lanes = <1 2>;
};
};
port@1 {
reg = <1>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
csidphy1_out: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&mipi2_csi2_input>;
};
};
};
};
&csi2_dphy2 {
status = "okay";
ports {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
port@0 {
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi_in_ucam3: endpoint@1 {
reg = <1>;
remote-endpoint = <&gc2093_out3>;
data-lanes = <1 2>;
};
};
port@1 {
reg = <1>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
csidphy2_out: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&mipi3_csi2_input>;
};
};
};
};
&mipi2_csi2 {
status = "okay";
ports {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
port@0 {
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi2_csi2_input: endpoint@1 {
reg = <1>;
remote-endpoint = <&csidphy1_out>;
};
};
port@1 {
reg = <1>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi2_csi2_output: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&cif_mipi_in2>;
};
};
};
};
&mipi3_csi2 {
status = "okay";
ports {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
port@0 {
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi3_csi2_input: endpoint@1 {
reg = <1>;
remote-endpoint = <&csidphy2_out>;
};
};
port@1 {
reg = <1>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
mipi3_csi2_output: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&cif_mipi_in3>;
};
};
};
};
&rkcif {
status = "okay";
};
&rkcif_mipi_lvds2 {
status = "okay";
port {
cif_mipi_in2: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&mipi2_csi2_output>;
};
};
};
&rkcif_mipi_lvds2_sditf {
status = "okay";
port {
mipi2_lvds_sditf: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&isp0_vir2>;
};
};
};
&rkcif_mipi_lvds3 {
status = "okay";
port {
cif_mipi_in3: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&mipi3_csi2_output>;
};
};
};
&rkcif_mipi_lvds3_sditf {
status = "okay";
port {
mipi3_lvds_sditf: endpoint {
remote-endpoint = <&isp1_vir0>;
};
};
};
&rkcif_mmu {
status = "okay";
};
1.3.4. Configure Isp¶
The remote-endpoint in rkisp_vir2 node should point to mipi2_lvds_sditf.The remote-endpoint in rkisp1_vir0 node should point to mipi3_lvds_sditf
&rkisp0 {
status = "okay";
};
&isp0_mmu {
status = "okay";
};
&rkisp1 {
status = "okay";
};
&isp1_mmu {
status = "okay";
};
&rkisp0_vir2 {
status = "okay";
port {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
isp0_vir2: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&mipi2_lvds_sditf>;
};
};
};
&rkisp1_vir0 {
status = "okay";
port {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
isp1_vir0: endpoint@0 {
reg = <0>;
remote-endpoint = <&mipi3_lvds_sditf>;
};
};
};
1.5. Single Camera CAM-8MS1M/Dual Camera CAM-2MS2MF¶
Firefly has already configured these cameras in dts, CAM-8MS1M and CAM-2MS2MF cannot be used at the same time. Only need to include specific dtsi file to use CAM-8MS1M or CAM-2MS2M.
1.5.1. Use Single Camera CAM-8MS1M¶
dts configured single camera as default.
diff --git a/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts b/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts
index 7e2a8b2..14fa027 100755
--- a/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts
+++ b/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts
@@ -7,6 +7,15 @@
+#include "rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q-cam-8ms1m.dtsi"
1.5.2. Use Dual Camera CAM-2MS2MF¶
diff --git a/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts b/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts
index 7e2a8b2..14fa027 100755
--- a/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts
+++ b/kernel/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q.dts
@@ -7,6 +7,15 @@
-#include "rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q-cam-8ms1m.dtsi"
-//#include "rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q-cam-2ms2mf.dtsi"
+//#include "rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q-cam-8ms1m.dtsi"
+#include "rk3588-firefly-aio-3588q-cam-2ms2mf.dtsi"
1.6. Camera Debug¶
Find the camera node
# Since a board may have multiple cameras, for cameras using RKISP such as 8Mega Pixel HD Camera(IMX415),
# it is necessary to use the video node named rkisp_mainpath.
# For cameras with their own ISP, such as 8Mega Pixel HD Camera,
# it is necessary to use the video node named stream_cif_mipi_id0.
root@firefly:~# grep '' /sys/class/video4linux/video*/name
/sys/class/video4linux/video0/name:stream_cif_mipi_id0
/sys/class/video4linux/video1/name:stream_cif_mipi_id1
/sys/class/video4linux/video10/name:rkcif_tools_id2
/sys/class/video4linux/video11/name:stream_cif_mipi_id0
/sys/class/video4linux/video12/name:stream_cif_mipi_id1
/sys/class/video4linux/video13/name:stream_cif_mipi_id2
/sys/class/video4linux/video14/name:stream_cif_mipi_id3
/sys/class/video4linux/video15/name:rkcif_scale_ch0
/sys/class/video4linux/video16/name:rkcif_scale_ch1
/sys/class/video4linux/video17/name:rkcif_scale_ch2
/sys/class/video4linux/video18/name:rkcif_scale_ch3
/sys/class/video4linux/video19/name:rkcif_tools_id0
/sys/class/video4linux/video2/name:stream_cif_mipi_id2
/sys/class/video4linux/video20/name:rkcif_tools_id1
/sys/class/video4linux/video21/name:rkcif_tools_id2
/sys/class/video4linux/video22/name:rkisp_mainpath
/sys/class/video4linux/video23/name:rkisp_selfpath
/sys/class/video4linux/video24/name:rkisp_fbcpath
/sys/class/video4linux/video25/name:rkisp_iqtool
/sys/class/video4linux/video26/name:rkisp_rawrd0_m
/sys/class/video4linux/video27/name:rkisp_rawrd2_s
/sys/class/video4linux/video28/name:rkisp_rawrd1_l
/sys/class/video4linux/video29/name:rkisp-statistics
/sys/class/video4linux/video3/name:stream_cif_mipi_id3
/sys/class/video4linux/video30/name:rkisp-input-params
/sys/class/video4linux/video31/name:stream_hdmirx
/sys/class/video4linux/video4/name:rkcif_scale_ch0
/sys/class/video4linux/video5/name:rkcif_scale_ch1
/sys/class/video4linux/video6/name:rkcif_scale_ch2
/sys/class/video4linux/video7/name:rkcif_scale_ch3
/sys/class/video4linux/video8/name:rkcif_tools_id0
/sys/class/video4linux/video9/name:rkcif_tools_id1
Use v4l2-ctl to capture camera frame data
v4l2-ctl --verbose -d /dev/video0 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080,pixelformat='NV12' --stream-mmap=4 --set-selection=target=crop,flags=0,top=0,left=0,width=1920,height=1080 --stream-to=/data/out.yuv
Copy file out.yuv to ubuntu to play
ffplay -f rawvideo -video_size 1920x1080 -pix_fmt nv12 out.yuv
1.7. Android Use Camera App¶
In addition to the official default supported cameras, To open camera with camera app in Android needs configuring in camera3_profiles*.xml. For details please refer to files in Android SDK under hardware/rockchip/camera/etc/camera.
1.8. Linux Preview Camera¶
Ubuntu firmware integrates test_camera-cifisp.sh test script. Script path /usr/local/bin/test_camera-cifisp.sh
#!/bin/sh
export DISPLAY=:0.0
#export GST_DEBUG=*:5
#export GST_DEBUG_FILE=/tmp/2.txt
echo "Start MIPI CSI Camera Preview!"
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/1000
if cat /proc/device-tree/model | grep -q "3588" ;then
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 io-mode=4 ! queue ! video/x-raw,format=NV12,width=1920,height=1080,framerate=30/1 ! glimagesink
else
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 io-mode=4 ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=NV12,width=640,height=480 ! rkximagesink
fi
1.9. IQ Files¶
Supported raw camera iq files are under external/camera_engine_rkaiq/iqfiles/isp3x. What’s different from before is that iq files will no longer use .xml files but .json files. Although there is a xml to json transfer tool, isp20 xml configuration are not suitable for isp3x even after transfer.
Similarly, the JSON of isp21 is not applicable to isp3x.
If you need to use raw sensor camera, please be careful about is there a matchable iq file under isp3x directory.
